The impurity-removed liquid after preliminary purification reacts with magnesium oxide slurry under certain conditions to generate cobalt hydroxide precipitate, and the reaction is as follows:
Mg(OH)2+CoSO4=Co(OH)2↓+MgSO4
In order to obtain high-grade cobalt hydroxide products and higher cobalt recovery rate, the condition test of active magnesium oxide usage was carried out to find out its influence on cobalt grade, cobalt recovery rate and pH, and determine the optimal amount of magnesium oxide. The experimental results are shown in Figures 2, 3 and 4.
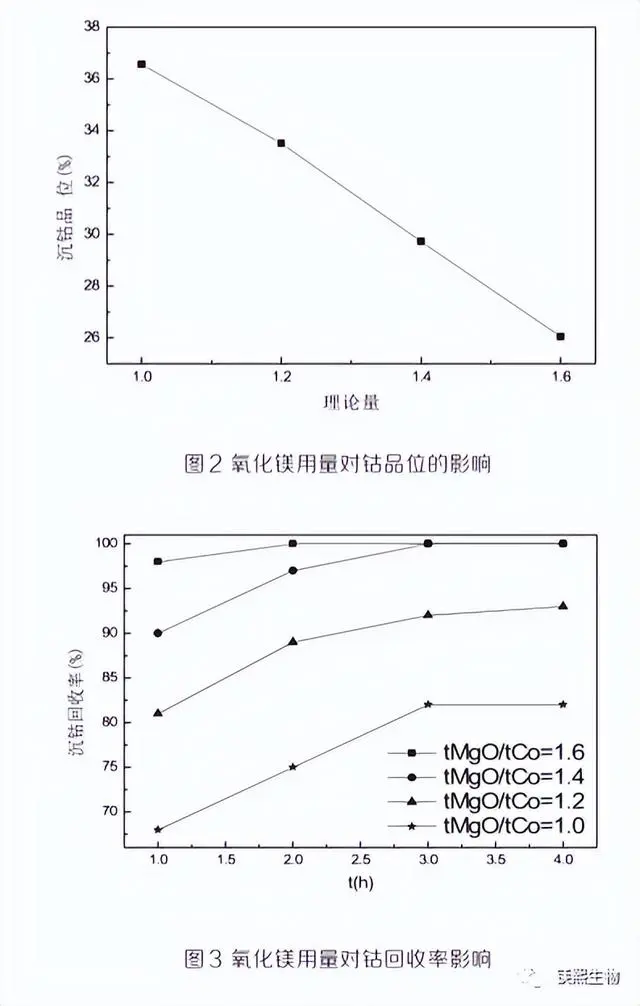
Experimental conditions: temperature 60℃, continuous stirring during the reaction, magnesium oxide slurry concentration 10%, and magnesium oxide addition amount 1.0, 1.2, 1.4 and 1.6 times the amount of cobalt metal in the solution.
As can be seen from Figure 2, with the increase of magnesium oxide usage, the cobalt grade in the cobalt hydroxide product gradually decreases. When the magnesium oxide usage is 1.0tMgO/tCo, the cobalt grade reaches the highest value of 36.4%. As can be seen from Figure 3, the more magnesium oxide is added, the higher the cobalt recovery rate of the first cobalt precipitation. When the magnesium oxide addition is 1.6tMg0/tCo, the cobalt recovery rate is almost 100%, but the cobalt grade of the cobalt hydroxide product is only 26%. As can be seen from Figure 3, the pH value of the solution increases with the extension of the reaction time, and within 1 hour after the start of the reaction, the pH of the solution rises rapidly. The pH value at the end of the reaction increases with the increase of magnesium oxide addition, and when the magnesium oxide addition is 1.0tMgO/tCo, the end pH is 7.3, and when the addition amount is other multiples, the end pH is above 8.0.
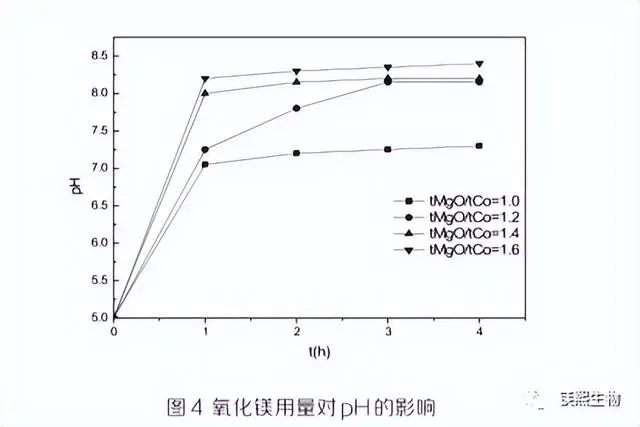
Based on the above, in the industrial trial production, the magnesium oxide usage is selected as 1.0 times the amount of cobalt metal in the solution. The industrial production data are as follows: the end pH of the first cobalt precipitation reaction is 7.2, the cobalt recovery rate is about 81.5%, and a higher grade cobalt hydroxide product is obtained, and its cobalt grade reaches 32.96%.
The typical composition of the liquid after the first cobalt precipitation is shown in Table 3. The typical composition of the cobalt hydroxide product after drying is shown in Table 4.
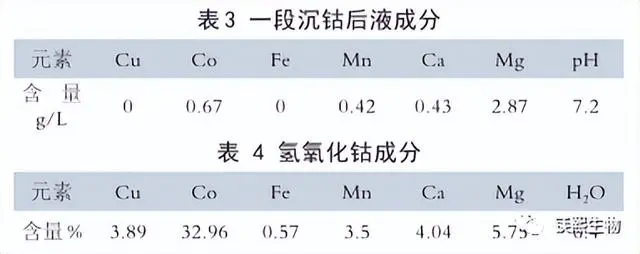
As shown in Table 3, the cobalt concentration in the liquid after the first stage of cobalt precipitation is still 0.67g/L, so it is necessary to carry out the second stage of cobalt precipitation to recover all the cobalt. As shown in Table 4, the magnesium content in the cobalt hydroxide product is relatively high, reaching 5.75%. After inspection and analysis, it was found that about 38% of the magnesium in the product exists in the form of magnesium sulfate, which is caused by the coprecipitation of magnesium sulfate with cobalt hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, etc. during the cobalt precipitation reaction. Therefore, a washing process can be added in production to use new water to wash the cobalt hydroxide to remove the soluble magnesium sulfate, thereby reducing the content of impurities such as magnesium in the cobalt product.
