1, Nano magnesium hydroxide properties
Nano magnesium hydroxide molecular formula Mg(OH)2, white microfine powder, non-toxic, odorless, non-corrosive, relative density 2.36, refractive index 1.561, 350 ℃ began to decompose, 430 ℃ decomposition is rapid, 490 ℃ when all decomposition, soluble in strong acid solutions and salt solutions according to the water, insoluble.
(1) Optical properties
When the grain size of metal materials is reduced to the nanometer level, the color changes to black and the particle size decreases. The light absorption capacity of nanoparticles is directly proportional to their color. The quantum size effect of energy levels and the charge distribution on the grain surface also affect the process of light absorption. The conduction electron energy levels in the grains often condense into very narrow energy bands resulting in narrow absorption bands. Nonlinear optical effects become another aspect of the study of optical properties of nanomaterials.
(2) Electromagnetic properties
The spacing of atoms in metallic materials is proportional to the change in particle size. Therefore, when a metal grain is in the nanometer range, its density increases as the spacing becomes smaller. As a result, the mean free range of the free electrons in the metal decreases and the conductivity decreases. In terms of magnetic structure, coarse-crystalline materials and nanomaterials are very different. In general, the magnetic structure of a magnetic material consists of many magnetic domains, which are separated from each other by domain walls, and the magnetization is achieved by the movement of the domain walls. In nanomaterials, when the grain size is smaller than a certain critical value, all the grains show a single magnetic domain structure, and the coercivity becomes significantly larger. When the grain size of nanomaterials decreases, the magnetic ordering state of the core material changes radically. For example, materials that are ferromagnetic in the coarse crystalline state can be transformed into a superparamagnetic state when the grain size is smaller than a certain critical value.
(3) Chemical catalytic performance
Due to the small particle size of nanomaterials, the number of atoms on the surface will occupy a large proportion, the adsorption capacity will be strengthened, and the chemical activity increases. Therefore, under the condition of room temperature, many metal nanomaterials are burned by violent oxidation reaction in the air. Electrodeless nanomaterials exposed to the atmosphere will adsorb gases and form adsorption layers. By utilizing this property, gas-sensitive progenitors can be made using nanomaterials to achieve detection of different gases. The catalytic properties of metallic nanomaterials are manifested in the catalytic breaking of H-H bonds, C-C bonds, C-O bonds, C-H bonds, etc. under suitable conditions. The main advantages of nanomaterials as catalysts include no fine pores, no heterogeneous components, free choice of components, mild conditions, and ease of use.
(4) Thermal properties
When the size of the constituent phases is small enough, changes in various elastic and thermodynamic parameters in the confined atomic system lead to changes in the equilibrium phases. The thermogravimetric experimental analysis shows that the melting point of copper nanoparticles with an average particle size of 40 nm decreases from 1053°C to 750°C. The melting point of the nanomaterials is less than that of the comparable coarse crystalline material, while the specific heat capacity is greater than that of the coarse crystalline material.
2、Use of nano magnesium hydroxide
Nano magnesium hydroxide has a wide range of uses, it can be used as flame retardant, preservative, food additives, acid and alkali neutralizer, flue gas desulfurization agent, heavy metal remover and so on.
(1) Flame retardant
Thermal decomposition of magnesium hydroxide produces magnesium oxide and a large amount of water vapor, the decomposition will absorb a large amount of heat, the release of water will reduce the temperature of the base material, and magnesium oxide can be used as a good flame retardant. The decomposition equation is as follows:
Mg(OH)2→MgO+H2O
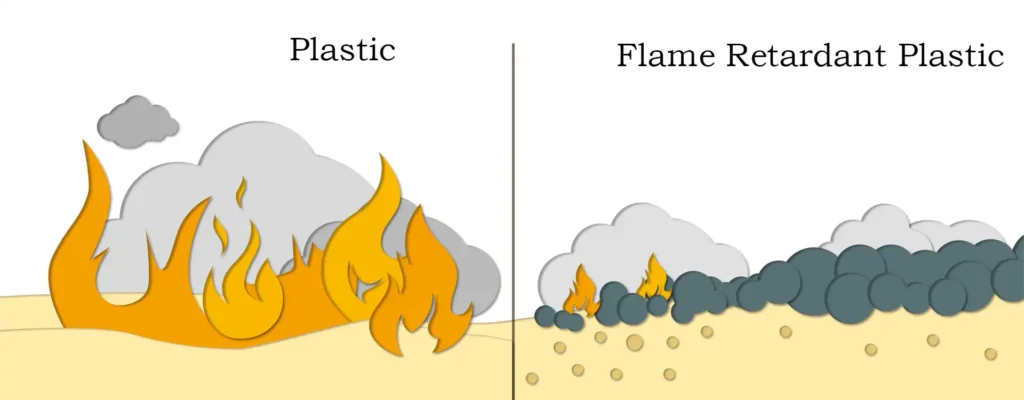
Using this principle, magnesium hydroxide is often added to polymer materials as a flame retardant. Due to the high thermal stability and decomposition temperature of magnesium hydroxide, as well as non-toxic, smoke suppression and other effects, often applied to engineering thermoset materials. Thermosetting engineering materials are generally processed at 220-250 ℃, adding a certain amount of magnesium hydroxide processing is safer and more reliable. When used as a flame retardant, the amount of ordinary magnesium hydroxide is large, and the filling amount reaches 40% to show a good flame retardant effect, which will affect the mechanical and mechanical processing properties of the base material. Through the surface modification, nano-grade magnesium hydroxide and the material has good compatibility, the physical and chemical properties of the base material has no effect, and play a role in enhancing the effect of complementary toughness.
(2) Preservative and food additives
Nano magnesium hydroxide can be used as a green food preservative. When a layer of magnesium hydroxide emulsion with a mass fraction of 3% is coated on the surface of potatoes for storage, it can effectively prevent the production of plant pathogens. Fish products treated with magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles not only prevent biodegradation of meat tissues, but also maintain their elasticity and softness. At the same time, nano magnesium hydroxide is also very safe and reliable as a food additive.

(3) Acid-base neutralizer and flue gas desulfurization agent
Magnesium hydroxide is a kind of weak alkali with unique buffering ability compared with other alkalis. When it is used as a neutralizer, even if it is in excess, the pH value of the solution will not exceed 9, and at the same time, its neutralization ability is strong, with the same concentration and volume of alkali compared to the efficiency is 30% higher. As a flue gas desulfurization agent, it has the characteristics of simple use process, easy to control and by-products can be recycled.
(4) Heavy metal remover

Nano-magnesium hydroxide particles have large specific surface area and high activity, so they have strong adsorption capacity, and can adsorb and remove Ni2+, Cd2+, Cr3+ and other heavy metal ions that cause harm to the environment from different industrial waste liquids. Sometimes nano magnesium hydroxide can also be used with lime and bentonite.
In addition, nano magnesium hydroxide can be used as a component of new mud materials in oil fields, and can also be applied in medical cosmetics, cigarette paper smoke inhibition coating, and magnetic material processing.
3, Nano-magnesium hydroxide synthesis method
(1) Precipitation method
Liquid phase precipitation method is a common method to prepare nanopowders. There are three kinds of liquid phase precipitation methods, which are direct precipitation method, uniform precipitation method, and co-precipitation method. The preparation of magnesium hydroxide using the liquid phase precipitation method mainly utilizes the reaction of a salt solution of magnesium ions with an alkali to produce a magnesium hydroxide precipitate. Commonly used salts are magnesium sulfate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, etc. Commonly used alkali precipitants are lime water, ammonia, hydroxide Na, urea, etc. Generally, the amount of precipitant is slightly excessive. This method does not require high equipment and technology, is easy to operate, is not easy to introduce impurities, the product is easy to purify, has good stoichiometry, and the preparation cost is low; however, the product particles are large and the particle size distribution is broad. Qiu Longzhen et al. used magnesium chloride hexahydrate and sodium hydroxide as raw materials, and prepared magnesium hydroxide nanopowder by surfactant-coated solution precipitation method, and its agglomeration phenomenon is not obvious.
(2) Hydrothermal method
Hydrothermal treatment method is to use water as a solvent, pour the raw materials into a closed container, control a certain temperature and pressure (the temperature is generally between the boiling point of water and the supercritical temperature, the pressure is generally 1-22 atmospheres), and carry out the chemical reaction method. In order to obtain the required special crystal shape and uniform particle size of Mg (OH) 2 is usually the synthesized magnesium hydroxide at room temperature is hydrothermally modified, the specific method is in the high temperature and high pressure of water solution, magnesium hydroxide through the dissolution, re-coalescence, recrystallization of the process to generate the required specific structure and morphology of magnesium hydroxide. The reason why the hydrothermal method can change the structure and morphology of the crystal is that under high temperature and high pressure, the water adsorbed on the surface of the crystal is chemosynthesized, destroying the liquid on the surface of the crystal, and the resistance of the crystal to grow up is reduced, which makes it conducive to the generation of crystals with larger crystal particles and smaller specific surface area of the special crystalline type, and the structure of such crystals is stable, and the phenomenon of agglomeration has been significantly improved. Lin Huibo et al. synthesized nano-sized, flaky, homogeneous and well-dispersed magnesium hydroxide powders with powder particle size less than 100 nm by hydrothermal method using magnesium chloride and sodium hydroxide as raw materials. Hydrothermal method generally requires high conditions, expensive equipment, the particle size of the product will generally increase, not conducive to industrial production.
(3) Precipitation – azeotropic distillation method
Precipitation – azeotropic distillation method refers to the use of chemical precipitation synthesized magnesium hydroxide first at room temperature and pressure conditions, after settling, washing the cake obtained with a specific solvent mixing slurry, and then heated to raise the temperature of the slurry in the solvent and water formed by the azeotropic material for evaporation, and continue to raise the temperature of the solvent to the boiling point of the solvent, so as to evaporate out of the solvent. Commonly used solvents include n-butanol, n-pentanol, etc., but n-butanol is commonly used as the azeotropic solvent. Dai Yanlin et al. pulped magnesium hydroxide powder with a certain amount of distilled water and n-butanol, and used the azeotrope formed by the water and n-butanol to distill and evaporate the water and n-butanol, to obtain nanoscale magnesium hydroxide powder. Using this method can synthesize uniformly dispersed nano magnesium hydroxide powder, can effectively remove the water in the magnesium hydroxide colloid, to overcome the generation of hard agglomeration.
(4) Electrolysis method
Electrolysis method is generally electrolysis of brine, the use of its by-products of sodium chloride, sodium chloride electrolysis produces precipitant sodium hydroxide, which is used to precipitate magnesium chloride, caustic soda dosage is greatly reduced, this method is suitable for the preparation of high purity, high yield of magnesium hydroxide, but it consumes a lot of electricity, does not conform to the national energy-saving and consumption reduction policy, pollution of the environment, the region of electric power constraints are also not suitable. Its main reaction equation is as follows.
MgCl2+2NaOH→Mg(OH)2+2NaCl
2NaCl+2H2O→2NaOH+H2+Cl2↑



