Messi Biology said that magnesium hydroxide is a new type of filler flame retardant, through the thermal decomposition of the release of bound water, absorbing a large amount of latent heat to reduce the surface temperature of the synthetic material it fills in the flame, with the inhibition of the decomposition of polymers and the resulting combustible gases to cool the role of the flame.
Definition of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant
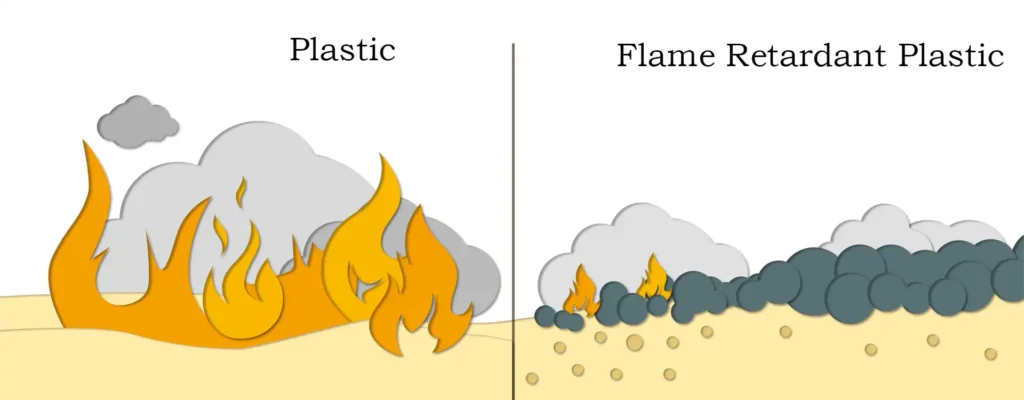
The magnesium oxide generated by decomposition is also a good refractory material, which can also help to improve the fire resistance of synthetic materials, while the water vapor it emits can also be used as a smoke suppressant. Magnesium hydroxide is recognized as an excellent flame retardant in the rubber and plastic industry with the triple functions of flame retardant, smoke suppressant and filler. It is widely used in rubber, chemical industry, building materials, plastics and electronics, unsaturated polyester and paints, coatings and other polymer materials. Especially for mining wind guide coated cloth, PVC whole core transport belt, flame retardant aluminum composite panel, flame retardant tarpaulin, PVC wire and cable materials, mining cable sheath, cable accessories flame retardant, smoke suppression and antistatic, can replace aluminum hydroxide, with excellent flame retardant effect. Magnesium hydroxide has better smoke suppression effect compared with similar inorganic flame retardants. Magnesium hydroxide in the production, use and disposal process are no harmful substances emission, but also can neutralize the acidic and corrosive gases produced in the combustion process. When used alone, the dosage is generally 40% to 60%.
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant development
Magnesium hydroxide is an inorganic flame retardant filler for polymer-based composites with good application prospects. Like aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide flame retardant relies on chemical decomposition when heated to absorb heat and release water to play a role in flame retardant, so it has the advantages of non-toxic, low smoke and decomposition of magnesium oxide generated by the stability of the chemical nature of the magnesium oxide, does not produce secondary pollution and so on. However, compared with halogen-containing organic flame retardants, in order to achieve a comparable flame retardant effect, the amount of filler is generally more than 50%. As magnesium hydroxide is inorganic, the surface and polymer base material compatibility is poor, such a high filling amount, if not for its surface modification treatment, filled into the polymer material, will lead to the mechanical properties of the composite material decline. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out surface modification treatment to improve its compatibility with the polymer base material, so that the mechanical properties of the filler material do not decline, and even make some of the mechanical properties of the material improved.
Experiments have proved that unmodified magnesium hydroxide exists in PP in the form of agglomerates, and although the powder itself is extremely fine, due to the incompatibility of the particle surface with the PP matrix, there are obvious boundaries or even voids between the particle agglomerates and the PP matrix. Because of the cavity formed after the escape of magnesium hydroxide particles during the brittle fracture, it indicates that the unmodified magnesium hydroxide in PP just plays a role of filling flame retardant, without chemical bonding with PP. After surface modification of magnesium hydroxide in the PP matrix dispersed uniformly, the particles are mostly in the form of primary particles or small agglomerated particles dispersed in the material.
Magnesium hydroxide related policies
China formulated the industry standard (HG/T3607-2000) on industrial powdered magnesium hydroxide in December 2000 and started to implement it on December 1 of the same year, and the HG/T3607-2007 standard is currently adopted. This is the only professional standard seen so far. Foreign different specifications and varieties of magnesium hydroxide production scale is very large, in different areas of the application of nearly 20 years of history, but has not been seen by the official put forward by the introduction of any standard. Therefore, our industry standard is very pioneering.
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant mechanism
Magnesium hydroxide when heated (340-490 degrees) decomposition occurs to absorb the heat of the surface of the burning material to the flame retardant effect; at the same time release a large amount of water to dilute the oxygen on the surface of the burning material, decomposition of active magnesium oxide generated by the surface of the combustible material attached to the combustible material to further prevent the combustion of the combustion. Magnesium hydroxide in the whole flame retardant process not only does not have any harmful substances, and its decomposition products in the flame retardant at the same time can also be a large number of absorption of rubber, plastics and other polymer combustion of harmful gases and smoke, activated magnesium oxide continues to absorb incomplete combustion of the melting residue from the combustion will soon stop at the same time eliminating smoke, preventing the melting of the droplets, is a kind of emerging environmentally friendly inorganic flame retardants.
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant classification
Flame retardants can be divided into two major categories according to their chemical composition: organic flame retardants and inorganic flame retardants. Organic flame retardants are divided into two series: phosphorus and halogen. Due to the existence of organic flame retardants decomposition product toxicity, smoke and other shortcomings, is gradually replaced by inorganic flame retardants.
The main varieties of inorganic flame retardants are aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, red phosphorus, antimony oxide, tin oxide, molybdenum oxide, ammonium molybdate, zinc borate, etc., of which aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide due to the decomposition of the absorption of heat and produce H2O can play a role in isolation of the air, and its decomposition of oxides and high-temperature-resistant substances, so the two kinds of flame retardant not only to play a role in fire-retardant, but also to play a role in filling, which does not have the production of corrosive halogen gas and hazardous gases, but also has the following features It has the characteristics of not producing corrosive halogen gas and harmful gases, non-volatile, long-lasting effect, non-toxic, non-smoke, non-dripping and so on.
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant preparation before use
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant in the application stage may be some accidents, so in the use of the former on the incomparable to do a good job of full preparation, not only can improve the flame retardant flame retardant effect, but also to make the whole process more secure, to pay attention to the following matters:
1. Sample test before flame retardant. Need to take some samples for flame retardant test, the purpose of this is mainly to test whether the flame retardant can meet the flame retardant standards and to test whether the flame retardant is suitable for the flame retardant material, so as not to waste the flame retardant.
2. The surface of the substrate should be properly cleaned before flame retardant, and the surface should be free from oil, water and dust.
3. Before flame retardant to understand the flame retardant use, temperature and flame retardant time, so as not to waste flame retardant and material.
Messi Biology said, in order to prevent the flame retardant is wasted and safety issues occur, before and after the use of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant these are the need to pay enough attention.

