Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) is one of the commonly used and preferred magnesium sources for the synthesis of Magnesium Glycerophosphate (MGP). It exhibits a series of advantages when used in the synthesis reaction:
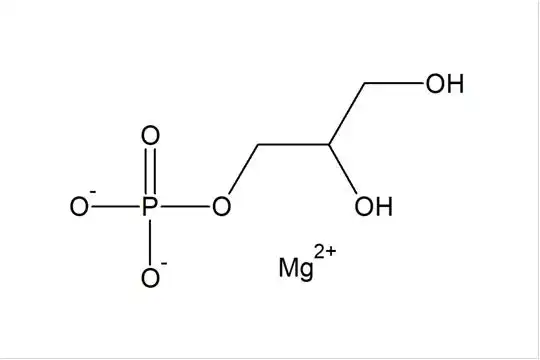
I. Reaction Principle and Pathway
Magnesium glycerophosphate is an organic magnesium salt produced by the reaction of glycerophosphoric acid (or its salts) with a magnesium-containing compound. As an alkaline magnesium source, magnesium hydroxide can directly undergo a neutralization and complexation reaction with glycerophosphoric acid to form a stable magnesium salt. The reaction is as follows:
Mg(OH)₂ + 2H₂PO₄C₃H₇O₃ → Mg(C₃H₇O₆P)₂ + 2H₂O
This reaction can proceed under mild conditions, with water as the only by-product, making it suitable for the green manufacturing requirements of food and pharmaceutical-grade products.
II. Comparative Advantages over Other Magnesium Sources
Compared to other common magnesium sources such as magnesium carbonate and magnesium oxide, magnesium hydroxide offers the following significant advantages:
- Milder reaction, avoiding strong exothermic effects: The reaction with magnesium oxide requires heat for activation, while magnesium carbonate releases CO₂ gas. In contrast, the reaction with magnesium hydroxide is smooth, can be carried out with stirring at room temperature, and is easy to control.
- Fewer impurities, leading to higher purity: High-quality magnesium hydroxide products typically have very low levels of impurities (such as heavy metals and carbonates), which facilitates the production of high-purity magnesium glycerophosphate.
- Better dissolution properties: The resulting magnesium salt’s solubility can be more easily controlled to fall within the range specified by pharmacopoeias, enhancing the absorption efficiency of oral formulations.
III. Adjustable Reaction Conditions and Strong Adaptability
The dosage of magnesium hydroxide, stirring speed, reaction time, and pH adjustment all have a direct impact on the quality of the final product. By regulating these parameters, it is possible to precisely control key properties of the resulting magnesium glycerophosphate, such as its crystal form, particle size, solubility, and pH value. This facilitates subsequent process development and large-scale production.
IV. Suitability for Food/Pharmaceutical Use
Magnesium hydroxide itself is widely used as a food additive and in pharmaceuticals (e.g., as an antacid and a laxative). Its safety and regulatory compliance have been well-established. Therefore, using magnesium hydroxide for the preparation of magnesium glycerophosphate meets the strict requirements for products to be non-toxic, have low residual levels, and be free of unwanted by-products.
