Messi Biology states that while plastic products are ubiquitous in daily life, they also bring potential fire hazards. As an environmentally friendly and efficient flame retardant, magnesium carbonate is quietly providing “fireproof suits” for plastics, building safety barriers in sectors such as construction, automotive, and electronics. This white powder, derived from natural magnesite, has become an ideal alternative to traditional toxic flame retardants due to its unique flame-retardant mechanism and multiple advantages.
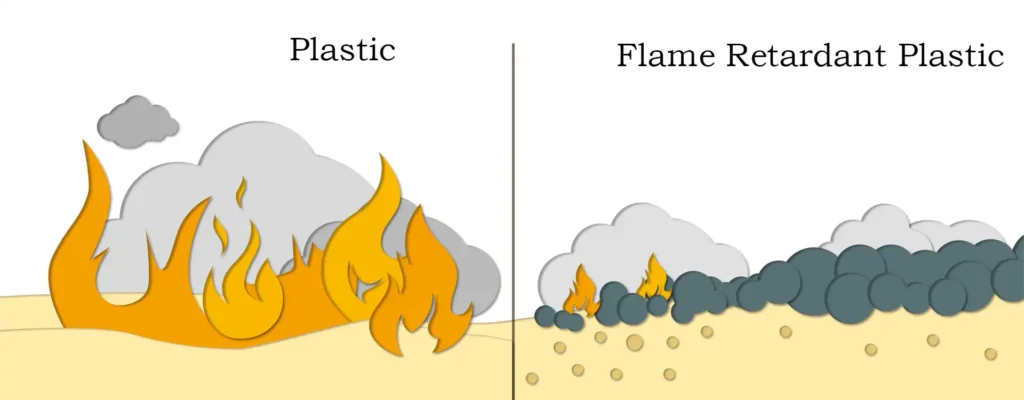
The flame-retardant capability of magnesium carbonate stems from its “triple protection” mechanism. When the temperature reaches approximately 350°C, it triggers an endothermic decomposition reaction, releasing carbon dioxide and producing magnesium oxide. This process absorbs a significant amount of heat, rapidly lowering the surface temperature of the plastic and delaying the onset of combustion. The released carbon dioxide dilutes the flammable gases and oxygen in the air, forming a “gas-phase barrier.” Meanwhile, the resulting magnesium oxide condenses into a dense char layer on the plastic surface, acting like armor to isolate heat and oxygen and prevent the spread of fire. This synergistic effect of “heat absorption, oxygen isolation, and coverage” allows it to effectively curb fire in its early stages, buying precious time for evacuation.
Compared to traditional antimony-based and halogen-based flame retardants, the environmental advantages of magnesium carbonate are particularly prominent. It contains no heavy metals or toxic components and does not produce highly toxic fumes such as dioxins or hydrogen chloride during combustion. It complies with international environmental standards such as RoHS and REACH, making it especially suitable for sensitive fields like food packaging and children’s toys. In terms of processing compatibility, magnesium carbonate exhibits excellent thermal stability and is perfectly compatible with the processing temperatures of plastics like PVC and PP, avoiding issues such as foaming or degradation caused by premature decomposition. Through nano-modification or surface coating treatments, its dispersibility can be further improved, minimizing the impact on the tensile strength and toughness of the plastic.
In practical applications, magnesium carbonate is widely used across multiple sectors. In the construction field, adding 15%-25% magnesium carbonate to PVC cables, flooring, and wall panels can meet the GB8624 fire safety standards while ensuring low smoke and low toxicity, thereby enhancing building safety levels. In automotive interior parts and electronic equipment shells, it is used in combination with magnesium hydroxide and phosphorus-based flame retardants to achieve a UL94 V-0 flame-retardant rating while meeting industry requirements for low-smoke and environmental protection. In household appliance shells and children’s toys, light magnesium carbonate, with its high dispersibility and low addition levels, maintains the appearance and mechanical properties of the products while ensuring flame-retardant performance.
Hebei Messi Biology Co., Ltd. notes that as flame-retardant standards continue to upgrade, “full-temperature range protection” solutions—compounding magnesium carbonate with magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide—are becoming increasingly popular. These solutions address initial flame retardancy while ensuring high-temperature stability, providing more comprehensive protection for plastic safety. This flame-retardant material, which combines environmental friendliness, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, is driving the plastic industry toward a safer and more sustainable future.
