Hexagonal sheet magnesium hydroxide is a typical layered inorganic material with a unique hexagonal sheet crystal structure. Its crystal structure determines its excellent physical and chemical properties, such as high thermal stability, electrical insulation and good flame retardant properties.
1. Basic characteristics of crystal structure
Magnesium hydroxide belongs to a layered hydrotalcite material, and its crystal structure is mainly composed of magnesium ions (Mg²⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻), forming a layered structure similar to aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)₃) and nickel hydroxide (Ni(OH)₂).
Unit cell parameters: The crystals of magnesium hydroxide belong to the Hexagonal system and the space group is P3m1.
Interlayer binding force: Hydroxide ions (OH⁻) form an octahedral structure around magnesium ions (Mg²⁺). The layers mainly rely on hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces to bond, so they are easy to peel off to form a nanosheet-like structure.
Layer spacing: The layer spacing of standard magnesium hydroxide is about 0.47 nm, but can be adjusted by intercalation or modification.
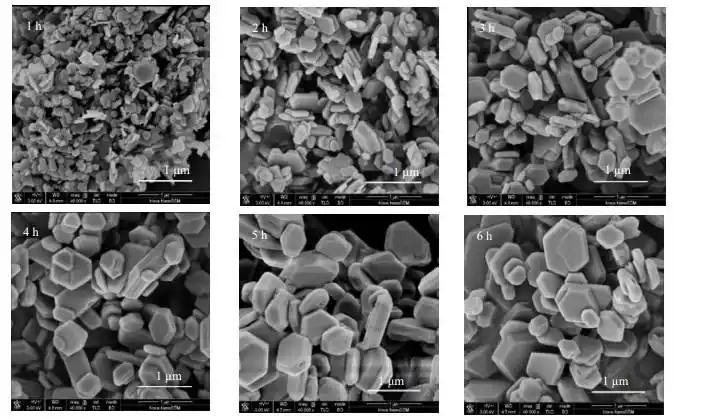
2. The formation mechanism of hexagonal sheet morphology
The formation of hexagonal sheet magnesium hydroxide is affected by crystal anisotropic growth, and its growth mechanism is mainly controlled by the Ostwald maturation process:
In aqueous solution, Mg²⁺ combines with OH⁻ to form Mg(OH)₂ nuclei.
As the reaction time is longer, the crystals are longer in a specific direction, and eventually form a layered structure.
Since the (001) plane of the hexagonal crystal system has the lowest surface energy, it grows slowly on the (001) plane and faster in the (100) and (110) plane directions, eventually forming a hexagonal sheet morphology.
3. Effect of crystal structure of hexagonal sheet magnesium hydroxide on performance
Due to its unique layered structure, hexagonal sheets of magnesium hydroxide exhibit the following excellent characteristics:
High specific surface area: Enhanced adsorption capacity and has application potential in the fields of catalysis and water treatment.
Good dispersibility: It has better dispersibility in polymer than traditional granular magnesium hydroxide, and is suitable as an inorganic filler.
Excellent flame retardant performance: its layered structure dehydrates at high temperatures to form MgO, which helps insulate heat and smoke suppression.
Enhanced mechanical properties: In composite materials, the toughness and heat resistance of the material can be improved.
4. Characterization method of hexagonal sheet magnesium hydroxide
In order to confirm the crystal structure of hexagonal sheet magnesium hydroxide, the following characterization methods are usually used:
X-ray diffraction (XRD) – Determines the crystal structure and layer spacing.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) – Observe sheet morphology and size distribution.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) – Analyzing the hexagonal structure and layered characteristics of crystals.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) – determines the presence and surface modification of hydroxide groups.
