Magnesium carbonate trihydrate (MgCO3·3H2O) is an important inorganic compound with a wide range of applications in pharmaceuticals, construction and lightweight materials. Its crystallization kinetics are crucial to controlling its final properties.
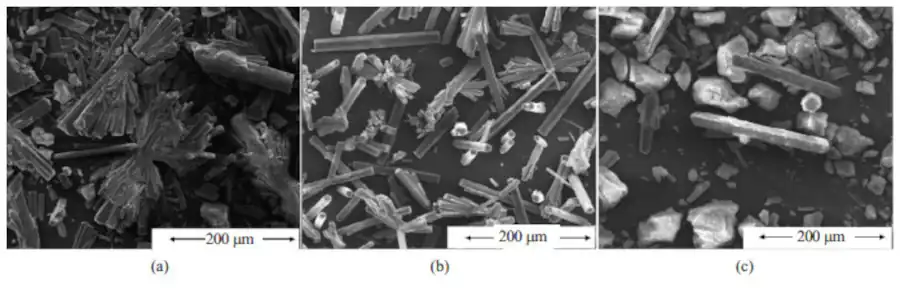
Effect of microwave irradiation:
Microwaves are high-frequency electromagnetic waves, and their irradiation causes the vibration of polar molecules inside the material. This vibration generates local heat, which can affect the crystallization process.
Enhanced nucleation and growth: Microwave energy can directly act on the solvent molecules in the reaction medium, resulting in local rapid heating, promoting the dissolution and diffusion of solutes, and accelerating the nucleation process. At the same time, the non-thermal effect of microwaves may also change the growth mechanism of the crystal, affecting the crystal morphology and size distribution.
Controlling grain size and morphology: Microwave irradiation can produce non-uniform thermal effects, resulting in temperature changes between different grain regions. This can affect the grain growth rate, thereby controlling the final size and morphology of the crystal.
Changing the crystal phase: Microwave irradiation can affect the final crystal phase formed. For example, studies have shown that microwave irradiation can promote the transformation of magnesium carbonate trihydrate into a dehydrated magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) crystal phase.
Energy saving: Compared with traditional heating methods, microwave irradiation is a more energy-efficient technology because it can transfer energy directly to the material and reduce heat loss. Compared with traditional heating methods, microwave heating rate is fast and can achieve the required crystallization conditions in a shorter time, greatly shortening the crystallization cycle and improving production efficiency.
Conclusion:
Microwave irradiation is an effective technology that can affect the crystallization kinetics of magnesium carbonate trihydrate. By controlling microwave parameters and solution conditions, the size, morphology, phase and properties of the crystals can be optimized. This is of great significance in various applications, from materials science to pharmaceuticals.
