- Physical barrier effect
When magnesium hydroxide decomposes by heat, it will release a large amount of water vapor. This water vapor will form a heat insulation layer on the surface of the material, blocking the transfer of heat to the inside of the material and reducing the burning rate of the material. At the same time, water vapor will also dilute the oxygen required for combustion and reduce the oxygen concentration in the combustion zone, thereby achieving a flame retardant effect.
- Chemical flame retardant effect
When magnesium hydroxide decomposes when heated, it produces magnesium oxide. Magnesium oxide is a refractory material that can cover the surface of the material to form a protective layer to prevent further combustion of the material. At the same time, magnesium oxide will also react with the acidic gases produced during the combustion process to form stable salts, reducing the smoke and harmful gases produced during the combustion process.
- Dilution
Magnesium hydroxide is an inorganic filler. When added to combustibles, it will dilute the content of combustibles and reduce the burning rate of combustibles.
- Catalytic carbonization
Magnesium hydroxide can catalyze the carbonization of combustibles, causing the combustibles to quickly form a carbon layer during the combustion process. The carbon layer can isolate oxygen and hinder the continuation of combustion.
- Reduce heat release rate
Magnesium hydroxide has a high heat capacity and will absorb a large amount of heat when heated, reducing the heat release rate of the material, thereby delaying the burning of the material.
- Smoking suppression effect
Magnesium hydroxide releases a large amount of water vapor during the combustion process, which can dilute the smoke and reduce the concentration and toxicity of the smoke.
In general, the flame retardant mechanism of magnesium hydroxide is the result of the combined action of multiple factors. Through physical barrier, chemical flame retardant, dilution, catalytic carbonization, reduction of heat release rate and smoke suppression, magnesium hydroxide can effectively reduce the burning rate of materials and improve the flame retardant properties of materials.
The flame retardant effect of magnesium hydroxide is affected by many factors, including the following aspects:
Particle size of magnesium hydroxide: The smaller the particle size, the larger the surface area and the better the flame retardant effect.
Surface modification of magnesium hydroxide: Surface modification of magnesium hydroxide can improve its compatibility with polymers and improve its dispersion, thereby improving the flame retardant effect.
Adding amount of magnesium hydroxide: The more added amount, the better the flame retardant effect, but it will also reduce the mechanical properties and processing performance of the material.
Type of polymer: Different types of polymers have different sensitivities to magnesium hydroxide, and their flame retardant effects will also vary.
Combustion environment: The combustion environment will also affect the flame retardant effect of magnesium hydroxide. Factors such as oxygen concentration and temperature will all have an impact on the flame retardant effect.
Applications of magnesium hydroxide
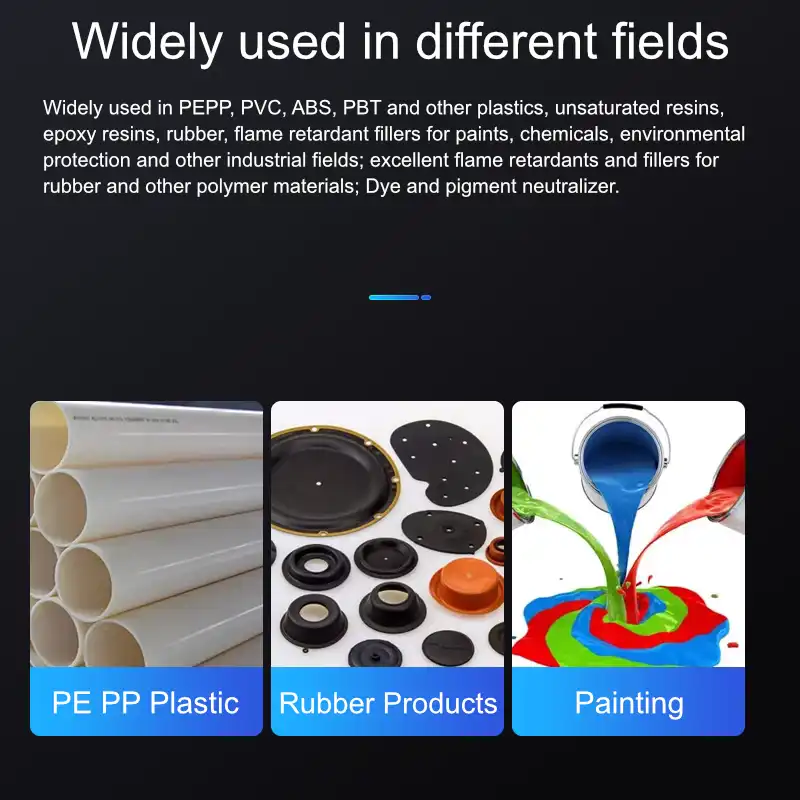
Magnesium hydroxide is widely used in rubber, plastics, wires and cables, building materials, textiles and other industries as an efficient and environmentally friendly flame retardant.

