Messi Biology states that high-purity magnesium oxide (MgO) is a critical functional material in the manufacturing of MLCCs (Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors). Its value is demonstrated by enhancing heat resistance, mechanical strength, and dielectric properties to meet the demands of high-end electronic devices. The industry has established clear purity standards (such as HG/T2573-2012) and optimized addition ratios (2–8%). With the growing demand for high-frequency and high-voltage MLCCs in 5G and new energy vehicles, the application of high-purity magnesium oxide is set to expand further.
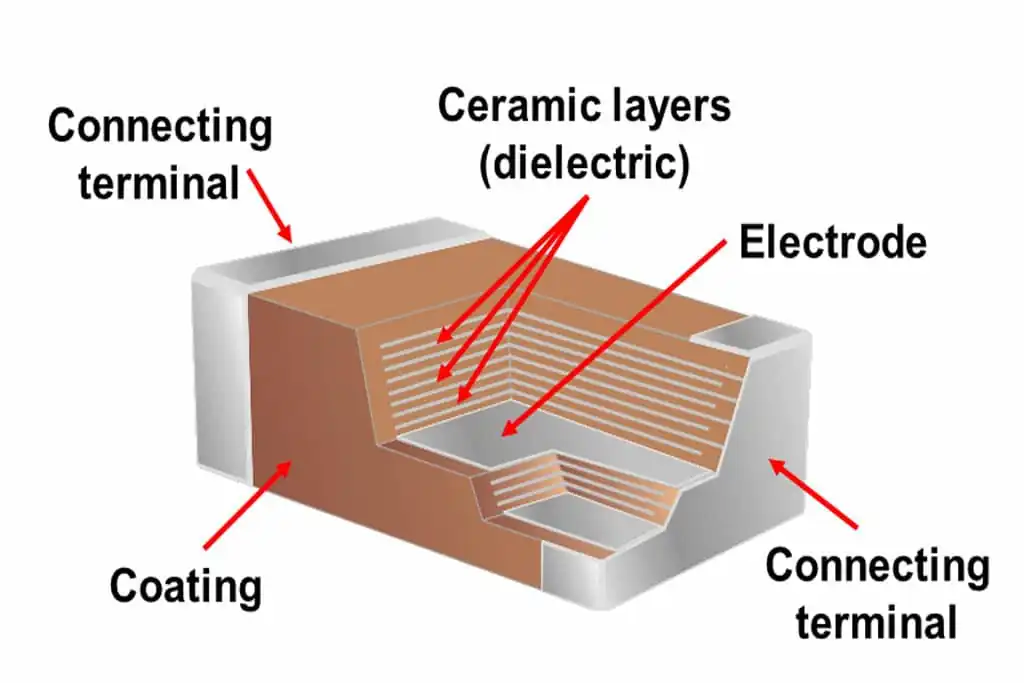
I. Basic Raw Material Composition of MLCCs
- Ceramic Dielectric Components
The ceramic dielectric of an MLCC is primarily composed of Barium Titanate (BaTiO3BaTiO_3BaTiO3), supplemented by other oxides such as Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2ZrO_2ZrO2) and Calcium Oxide (CaOCaOCaO). The composition varies depending on the type of MLCC:- C0G Class: Primarily based on Strontium Zirconate (
SrZrO3SrZrO_3SrZrO3) or Barium Strontium Titanate (BaSrTiO3BaSrTiO_3BaSrTiO3). These offer a stable dielectric constant and excellent temperature characteristics. - X7R/X5R Class: Based on Barium Titanate (
BaTiO3BaTiO_3BaTiO3), with rare earth oxides (e.g.,Y2O3Y_2O_3Y2O3) and transition metal oxides (e.g.,MgOMgOMgO,MnOMnOMnO) added to regulate dielectric performance.
- C0G Class: Primarily based on Strontium Zirconate (
- Role of Additives
Magnesium oxide (MgO), as a secondary component, is often added alongside Silicon Dioxide (SiO2SiO_2SiO2) and Calcium Oxide (CaOCaOCaO) to optimize sintering performance and dielectric properties.
II. Functions of High-Purity Magnesium Oxide in MLCCs
- Performance Optimization
- High-Temperature Resistance: MgO has a melting point as high as 2852°C, which improves the stability of MLCCs in high-temperature environments, allowing them to maintain electrical performance above 150°C.
- Mechanical Strength: By filling microscopic defects in the ceramic structure, it enhances material density and improves resistance to impact and wear.
- Electrical Insulation: It reduces ceramic conductivity and increases insulation resistance, making it suitable for high-voltage and high-frequency circuits.
- Process Improvement
- Sintering Aid: Magnesium oxide can lower the sintering temperature (to approximately 1320–1350°C), promote ceramic densification, and shorten production cycles.
- Dielectric Regulation: By adjusting the crystal structure, it optimizes the dielectric constant (
ϵ=9.8–10.2\epsilon = 9.8–10.2ϵ=9.8–10.2) and dielectric loss to meet the requirements of different MLCC models.
III. Technical Standards and Addition Ratios
- Purity Requirements
High-purity magnesium oxide must reach a MgO content of≥98%\ge 98\%≥98%(industrial grade) or≥99.9%\ge 99.9\%≥99.9%(electronic grade), with impurities such as calcium and iron controlled at the ppm (parts per million) level. - Typical Addition Amounts
- General-Purpose MLCCs: The addition ratio is typically 2–3 mol% (approx. 0.5–1.5 wt%). Excessive amounts may cause a decline in dielectric performance.
- High-Frequency MLCCs: The addition of nano-magnesium oxide (particle size < 500 nm) can be increased to 5–8% to improve high-frequency signal transmission loss.
IV. Application Cases and Industry Practices
- Practical Applications
- High-Voltage MLCCs: High-purity magnesium oxide from Messi Biology serves as an insulating medium, keeping dielectric constant fluctuations within
±2%\pm 2\%±2%and enhancing product consistency. - 5G Communication Devices: Adding 3–8% magnesium oxide to silicon nitride ceramic substrates optimizes thermal conductivity and signal integrity.
- High-Voltage MLCCs: High-purity magnesium oxide from Messi Biology serves as an insulating medium, keeping dielectric constant fluctuations within
- Differences by Type
- C0G Class: Magnesium oxide is mainly used to regulate the Curie temperature (
TcT_cTc). Every 1 mol% of MgO added to Barium Titanate lowers theTcT_cTcby 3–5°C, satisfying low-temperature stability requirements. - X7R Class: It acts as a grain boundary modifier to inhibit dielectric constant drift over temperature changes, ensuring that
ΔC/C≤±15%\Delta C/C \le \pm 15\%ΔC/C≤±15%.
- C0G Class: Magnesium oxide is mainly used to regulate the Curie temperature (
Recommendations
If specific formulas or process parameters are required, please refer to the technical manuals provided by electronic-grade magnesium oxide suppliers (such as Messi Biology) or adjust doping strategies based on the specific MLCC type (C0G/X7R).
