Magnesium oxide (MgO) is an inorganic substance with the chemical formula MgO.The following is a detailed analysis of magnesium oxide:
1, Physical Properties
Magnesium oxide is white powdery or amorphous powder, odorless, tasteless and non-toxic.
It has a density of 3.58g/cm³(25℃), a melting point of 2852℃ and a boiling point of 3600℃.
Magnesium oxide is insoluble in water, but its solubility in water (100°C) is 0.0048g/100g.
It is soluble in acids and ammonium salt solutions, while giving off heat and producing the corresponding magnesium salt.
Magnesium oxide is slightly soluble in ethanol but insoluble in acetone.
2, Chemical Properties
Magnesium oxide is a basic oxide and has the general properties of basic oxides.
It reacts with acids to form salts and water, e.g. with hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and water.
At high temperatures, magnesium oxide can react with a variety of reducing substances such as carbon, aluminum, zinc, silicon, iron, etc. in a replacement reaction to produce the corresponding metal magnesium or its alloys.
3, Uses
Magnesium oxide has shown significant potential for new applications in the biomedical field, especially in drug carriers, antimicrobial materials, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents, and bio-imaging. The following is an analysis of the new applications of magnesium oxide in biomedicine:

Drug carriers: magnesium oxide nanoparticles, due to their unique physicochemical properties and biocompatibility, can improve drug stability and bioavailability as drug carriers. It can be loaded with drugs by physical adsorption or chemical bonding to achieve slow release and targeted delivery of drugs, a characteristic that is of great significance in the fields of cancer treatment, cardiovascular disease treatment, etc.

Antimicrobial materials: magnesium oxide has broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and can effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi and viruses. It can be used as a coating for medical devices to reduce the risk of infection, or in the manufacture of antimicrobial dressings to promote wound healing.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AND ANTIOXIDANT: Magnesium oxide exhibits good anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in vivo, scavenging free radicals and mitigating oxidative stress damage, thereby protecting cells from inflammation and oxidative damage. This property gives it potential application in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases and autoimmune diseases.

Bio-imaging: With high optical contrast and biocompatibility, magnesium oxide nanoparticles can be used as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescence imaging, which can help improve diagnostic accuracy and sensitivity.
Antacids and laxatives: In the application of pharmaceutical grade magnesium oxide, it is widely used to make antacids and laxatives, which are used to neutralize gastric acid, protect ulcer surfaces, and play an important role in the production of gastric drugs.

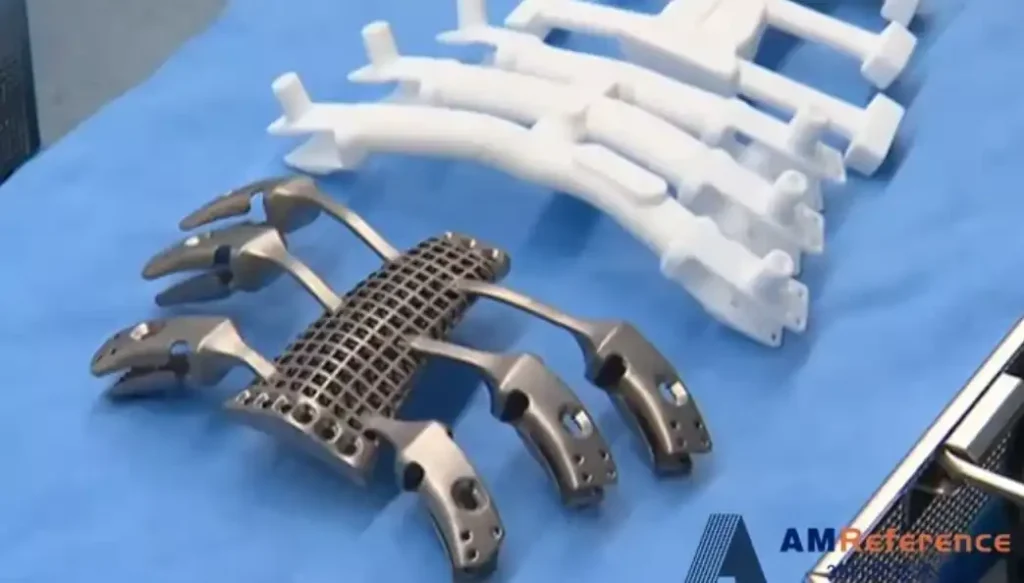
Tissue engineering: Magnesium oxide also shows potential in the field of tissue engineering, especially its excellent mechanical properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility, which makes it a strong candidate for modern implant materials.

In summary, magnesium oxide has a promising new application in the field of biomedicine, which not only improves the efficacy and stability of drugs, but also shows unique advantages in antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and bio-imaging. With the continuous development of nanotechnology, the application of magnesium oxide in the field of biomedicine will be more extensive, providing new ideas and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.

