Background and Overview
Colorless tetrahedral crystals or white powder, toxic. Insoluble in water and ethanol, easily soluble in nitric acid. Magnesium fluoride is a colorless tetragonal crystal or powder, soluble in nitric acid, slightly soluble in dilute acid, insoluble in water and alcohol; mainly used in the manufacture of ceramics, glass, smelting flux for magnesium and aluminum metals; and coatings for lenses and filters in optical instruments; it can also be used as a fluorescent material for cathode ray screens, a reflective refractor and welding agent for optical lenses. The traditional production method of magnesium fluoride is to use different magnesium salts to react with hydrofluoric acid, mainly magnesium carbonate method, magnesium oxide method, magnesium sulfate method, etc.

The traditional method is to use hydrofluoric acid and magnesium salts to react. Hydrofluoric acid is mainly produced by the reaction of fluorite and sulfuric acid. The traditional process consumes precious strategic resources fluorite. Now the country has increased its control over fluorite, and the price of fluorite is getting higher and higher. The corresponding price of hydrofluoric acid will inevitably increase, thereby affecting the cost of magnesium fluoride. Finding new fluorine sources to replace hydrofluoric acid is an important way to reduce the cost of magnesium fluoride and enhance its competitiveness. In addition, the existing process has a large amount of mother liquor discharged during the production process, which has a serious impact on the surrounding environment.
The purity of magnesium fluoride is greatly affected by magnesium salts. The main content of magnesium fluoride produced by using low-purity magnesium salts (magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide) can generally only reach 75%, which can only meet the requirements of additives for electrolytic aluminum and flux for smelting metal magnesium. If you want to meet the requirements of optical lenses and fluorescent materials, you need to use high-purity magnesium salts, and the indicators of the two types of magnesium fluoride are very different. At present, there is an urgent need to find a new magnesium salt to solve the high price of magnesium fluoride caused by the high price of high-purity magnesium salts.
Application
Magnesium fluoride is also used in ceramics and electronics industries; manufacturing ceramics and glass; flux for metallurgical magnesium metal; fluorescent materials for cathode ray screens; flux, etc. Magnesium fluoride is a colorless crystal or powder, an important inorganic chemical raw material, used as an additive for electrolytic aluminum, a flux for smelting metal magnesium, a coating agent for titanium pigments, and a fluorescent material for cathode ray screens. At the same time, it is also a colorless and transparent infrared optical material with a wide transmission range and high transmittance. It is used to make optical prisms, lenses and window elements in infrared optical systems.
With the widespread use of infrared technology in the military, optical instruments made of magnesium fluoride have many advantages such as high mechanical strength, strong thermal shock resistance, chemical corrosion resistance and isotropy in addition to good light transmittance in the medium-wave infrared band. It can be used as infrared temperature detectors, precision-guided missile fairings and infrared laser windows.
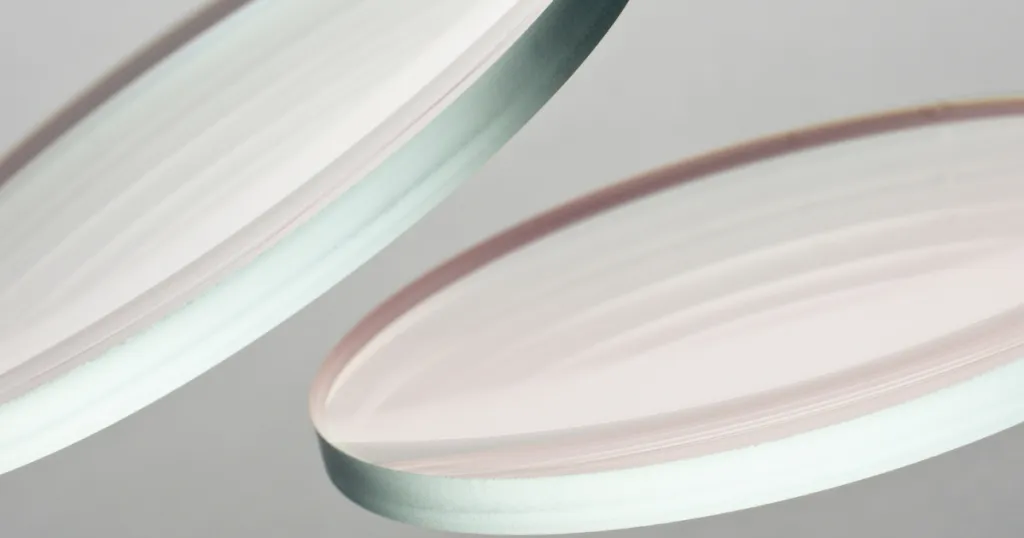

Since the 1960s, hot-pressed magnesium fluoride has been used in missiles guided by medium-wave infrared and infrared forward-looking windows, infrared pods, optoelectronic radars and other systems of aircraft. Among them, the more representative infrared missiles are the “Sidewinder” missiles of the United States, the missiles of Russia, the “Mistral” missiles of France, and the “Snake” missiles of Israel. Magnesium fluoride can be used for optical lens coating. Optical equipment coated with a layer of magnesium fluoride film can reduce the reflection of the incident light at the lens interface, reduce halo, and improve imaging quality.
Preparation
1. Magnesium carbonate method:
The magnesium source used in the preparation of magnesium fluoride by magnesium carbonate method is mostly dolomite or magnesite. The reaction equation is:
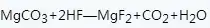
The process of preparing magnesium fluoride by magnesium carbonate method (using magnesite as raw material):
1) Add hydrofluoric acid to magnesite powder slurry, stir and react for a period of time to obtain magnesium fluoride slurry; the escaped gas is treated and discharged.
2) The magnesium fluoride slurry is filtered, and the filter residue is washed and dried to obtain the magnesium fluoride product; part of the filtrate is used for ore powder slurry, and part is sent to the treatment tank for neutralization with dilute magnesium carbonate, and discharged after meeting the standards.
2. Magnesium sulfate (or magnesium nitrate) method:
The magnesium sulfate (or magnesium nitrate) method is to prepare magnesium fluoride with magnesium sulfate or magnesium nitrate as raw materials, and the reaction formula involved is as follows:
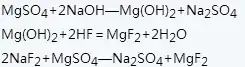
The process of preparing magnesium fluoride with magnesium sulfate (or magnesium nitrate) method (with magnesium sulfate as raw material):
1) Pre-treat the hydrated magnesium sulfate to remove some impurities;
2) React magnesium sulfate with alkali, wash and filter the obtained intermediate product, place it in a lead-lined or plastic-lined reactor, and react with excess hydrofluoric acid while stirring. This reaction requires maintaining a certain carbon dioxide partial pressure;
3) After the reaction is completed, wash, dry and crush the material to obtain a high-purity magnesium fluoride product.
3. Magnesium oxide method:
The magnesium oxide method uses magnesium oxide as raw material to prepare magnesium fluoride. The reaction formula is as follows:
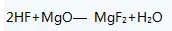
The process of preparing magnesium fluoride using magnesium oxide as raw material:
1) Place high-purity magnesium oxide with a mass fraction of 99.99% in a platinum crucible and cook with analytical pure hydrofluoric acid with a mass fraction of 40% to react and obtain magnesium fluoride slurry.
2) Refine and filter the magnesium fluoride slurry, then dry and crush it to obtain a high-purity magnesium fluoride product.
4. Magnesium chloride method:
Brine-ammonia-hydrofluoric acid method: The brine-ammonia-hydrofluoric acid method is used to prepare magnesium fluoride with magnesium chloride and ammonia as raw materials. The reaction formula is as follows:
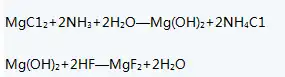
The process of preparing magnesium fluoride by brine-ammonia-hydrofluoric acid method:
1) Prepare MgCl2: into brine, then pass ammonia gas into the solution to generate Mg(OH)2 precipitation, filter, obtain Mg(OH)2 filter cake, and crush the filter cake.
2) Add a slightly excessive amount of hydrofluoric acid to the crushed filter cake. After the reaction is completed, filter and wash the material to remove the adsorbed HF, and dry to obtain MgF2, the finished product.
Ammonium fluoride-magnesium chloride method: The ammonium fluoride-magnesium chloride method is to prepare magnesium fluoride with ammonium fluoride and magnesium chloride as raw materials, and the reaction formula is as follows:

The process of preparing magnesium fluoride by ammonium fluoride-magnesium chloride method:
1) Add 30%-45% ammonium fluoride solution and 25%-36% magnesium chloride solution to the reactor at the same time, and obtain magnesium fluoride slurry after reaction, and filter to obtain magnesium fluoride ointment.
2) Wash the magnesium fluoride ointment with 60-70℃ hot water, then dry it at 250-400℃ for 1-2h, and crush it to obtain the finished magnesium fluoride.
5. Preparation of basic magnesium carbonate
The process of converting basic magnesium carbonate into pure magnesium fluoride is: contacting the basic magnesium carbonate suspension with CO2 to form sufficient magnesium dicarbonate or magnesium carbonate hydrate, and in this process, the particles of the suspension change. The carbonization of the suspension increases the solubility of the particles by establishing a balance between unstable magnesium dicarbonate and magnesium carbonate hydrate. During carbonization, the suspension is added to a sealed reaction barrel and reacted with a slightly excess of HF under stirring to precipitate fine magnesium fluoride particles. After the excess liquid is discharged with a siphon, the excess HF is neutralized with NH4OH. The precipitated particles can be dried and roasted to obtain magnesium fluoride powder.
The main chemical reaction formula of this method is:
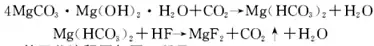
Fine granular, compressible ultra-pure magnesium fluoride powder can be directly obtained from basic magnesium carbonate and hydrofluoric acid. This powder has a specific uniform refractive index of 1.3850 at 20°C, and its particles are particularly uniform, and no grinding is required before hot pressing. The magnesium fluoride prepared by this method can be used in high-tech fields such as optical lens coating, advanced ceramics, and glass.
6. Liquid phase neutralization method
The liquid phase neutralization method uses soluble magnesium salt as the main raw material, adds ammonia water to generate the intermediate substance magnesium hydroxide, and reacts magnesium hydroxide with hydrofluoric acid to obtain magnesium fluoride.
The liquid phase neutralization method specifically includes the following steps:
① prepare a uniformly mixed soluble magnesium salt solution;
② introduce a certain amount of ammonia gas or add ammonia water, stir evenly and react to generate magnesium hydroxide, and place it for 24 hours;
③ remove excess magnesium chloride and ammonium chloride in the solution through suction filtration and washing to make the solution neutral;
④ add a certain amount of hydrofluoric acid to react to generate magnesium fluoride, and obtain the finished magnesium fluoride after filtration, washing and drying. The main chemical reaction formula is:
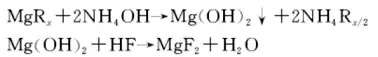
The impurities in the magnesium fluoride generated by this process are easy to clean and remove, so the purity of the finished magnesium fluoride is very high. The purity of magnesium fluoride prepared by this method using brine (the main raw material is magnesium chloride) produced as a by-product of salt extraction is 99.91%. Compared with the magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate methods, this method has high industrial value because magnesium chloride contains fewer impurities, magnesium hydroxide has a large particle size, is easy to wash, and has a low production cost. Using this process, magnesium fluoride with a purity of up to 99.999% can be prepared using medical high-purity magnesium sulfate heptahydrate as raw material, but the raw material cost is high and it is not suitable for large-scale industrial production. Therefore, the purity of magnesium fluoride prepared by the liquid phase neutralization method depends on the purity of the magnesium salt.
