Introduction
Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used thermoplastic, but its flammability severely limits its application in some fields. Basic magnesium carbonate (BCM) is an inorganic flame retardant that has received widespread attention in recent years due to its unique structure and decomposition behavior. This study aimed to investigate the performance of BCM flame retardant PP.

Experimental materials and methods
Raw materials: polypropylene powder, basic magnesium carbonate
Preparation method: basic magnesium carbonate is added to PP through a melt blending process.
Characterization methods: The flame retardant properties were characterized using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), cone calorimeter (DSC), and limiting oxygen index (LOI).
Results and discussion
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA curves show that the thermal stability of basic magnesium carbonate flame retardant PP is significantly improved compared to non-flame retardant PP. The weight loss temperature of PP increased from 410°C to 450°C with the addition of 10 wt% basic magnesium carbonate. This indicates that basic magnesium carbonate promotes the formation of degradation products of the polymer matrix and inhibits the thermal decomposition process.
Cone Calorimeter (DSC)
DSC curves revealed the effect of basic magnesium carbonate on PP combustion behavior. Basic magnesium carbonate flame retardant PP has lower peak heat release rate and total heat release compared to non-flame retardant PP. This suggests that basic magnesium carbonate inhibits the combustion release of polymers by reacting with free radicals or forming an insulating char layer.
Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI)
LOI is an important indicator of the flame retardancy of materials. The LOI of PP increased from 17.5% to 26.2% with the addition of 10 wt% basic magnesium carbonate. This indicates that basic magnesium carbonate effectively improves the flame retardancy of PP, allowing it to be extinguished at lower oxygen concentrations.
The mechanism of basic magnesium carbonate flame retardant PP may be due to the following factors:
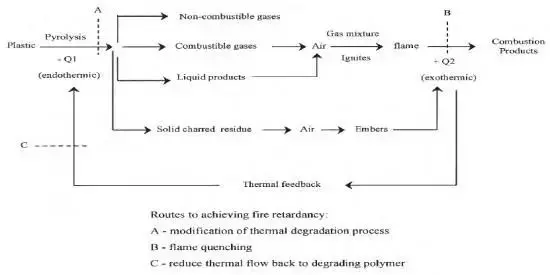
Energy absorption: basic magnesium carbonate decomposes under high temperature conditions, consuming heat.
Free Radical Capture: basic magnesium carbonate reacts with free radicals generated by polymer degradation, terminating the combustion reaction.
Carbon layer formation: basic magnesium carbonate decomposes at high temperatures to form stable MgO and CO2, forming an insulating carbon layer that isolates oxygen and hinders flame propagation.
in conclusion
This study shows that basic magnesium carbonate is an effective flame retardant and can significantly improve the flame retardant properties of polypropylene. Basic magnesium carbonate enhances the flame retardant capabilities of PP by improving thermal stability, reducing heat release rate, and increasing limiting oxygen index. Its unique decomposition behavior and char layer formation mechanism make it a promising inorganic flame retardant that can be used to improve the safety of PP in the field of fire protection.

