According to Messi Biology, magnesium oxide (MgO) is often used in metallurgical covering agents as a high-temperature resistant aggregate, auxiliary reaction material, or one of the main components. Its particle size distribution (PSD) directly affects the physical properties of the covering agent, its interfacial reaction behavior with the molten metal, and the stability of the covering layer.
Reasonably selecting magnesium oxide with different particle sizes can help to:
- Improve the density and thermal insulation of the covering layer.
- Control the melting rate and reaction activity of the covering agent.
- Optimize the balance between cost and performance.
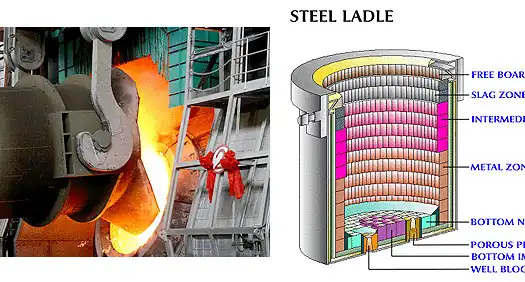
1. Covering Layer Density and Thermal Insulation
- Fine-particle magnesium oxide can fill the voids between large particles, increasing the density of the covering layer.
- A denser structure means better thermal insulation, reducing heat loss from the molten metal.
- However, excessively fine particles may absorb moisture and agglomerate, affecting storage and application.
2. Covering Agent Melting Speed and Adhesion
- Fine-grain magnesium oxide melts faster, which is beneficial for quickly forming a protective film.
- Coarse particles melt slower, making them suitable for long-lasting covering layers, applicable to high-temperature, long-duration casting scenarios.
- Using a mixture of particle sizes (bimodal distribution) can achieve a comprehensive effect of fast melting + stability.
3. Interfacial Reaction Behavior with Molten Metal
- Active magnesium oxide (fine powder) readily forms a reaction layer at the interface with the molten metal, improving the adsorption of impurities and the ability to purify inclusions.
- Coarse particles have poor reactivity but provide mechanical support, preventing the covering layer from collapsing or penetrating.
4. Covering Agent Flowability and Spreadability
- When the particle size is too fine, the flowability is poor and dust is easily generated.
- Appropriately combining medium-sized magnesium oxide can improve the spreading effect and enhance on-site operability.
5. Cost and Industrial Adaptability
- Fine-particle magnesium oxide (high activity) is more expensive.
- Coarse or medium-sized sintered MgO is relatively cheaper and suitable for large-scale applications.
- A mixed design with different particle sizes can balance cost and performance.
