What are the main uses of magnesium hydroxide?
【Overview】
Magnesium hydroxide is a hexagonal crystal system or amorphous flaky crystal, which is an inorganic weak alkaline product. Because of its strong buffering performance, high activity and adsorption capacity, safe handling and use, non-corrosiveness, non-toxicity, harmlessness and many other unique properties, it is known as “green and safe neutralizer”, “environmentally friendly flame retardant” and “the third alkali”. It is one of the favored and respected products in the process of promoting sustainable development strategy, protecting the environment and beneficial ecological development. It has a wide range of applications in ceramic materials, environmental protection, medicine and other fields. Among them, the main areas with large consumption and significant use effects are: first, as an inorganic additive non-toxic flame retardant, it has multiple properties such as flame retardancy, smoke suppression, anti-dripping, and filling; second, in the environmental field, it can be used for wastewater treatment and flue gas desulfurization; third, high-purity magnesium hydroxide is one of the most important raw materials for producing high-purity magnesium oxide.
【Physical and Chemical Properties】
Magnesium hydroxide is a white solid powder with the molecular formula Mg(OH)2 and a relative molecular weight of 58.33. It belongs to the hexagonal crystal system or amorphous flaky crystals with a density of 2.39g/cm3, a refractive index of 1.5611.581, a Mohs hardness of 23, and a volume resistivity of 108~1010 Ω·cm. It is sparingly soluble in water (solubility of 0.0009g/100mL at 18℃) and insoluble in a 1mol/L sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, but soluble in strong acidic solutions. When 2g of magnesium hydroxide is suspended in 50mL of water, the pH value of the system is 10.3.
【Uses】
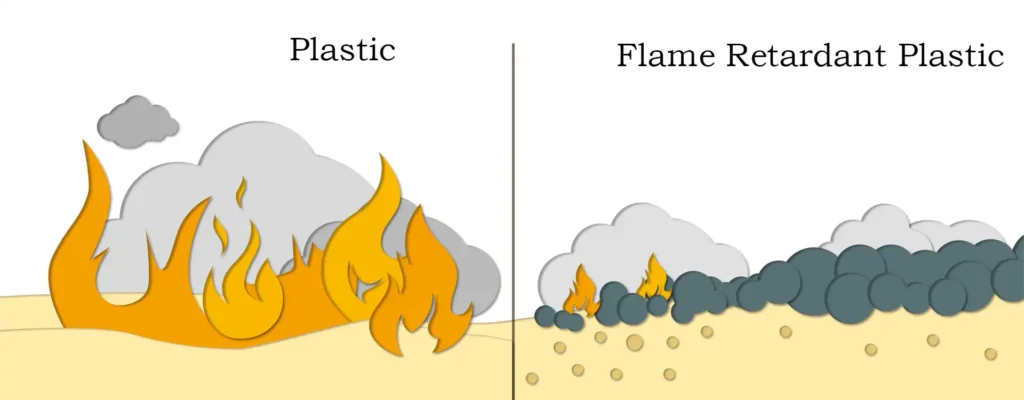
Magnesium hydroxide is both a product and an intermediate material in factories. As an intermediate material, it can be used to produce magnesium oxide. Ultra-fine magnesium hydroxide is also one of the important raw materials for producing nano-magnesium oxide. As a product, it has many uses, among which the main areas with large consumption and significant use effects are two: first, as an inorganic additive non-toxic flame retardant, it has multiple properties such as flame retardancy, smoke suppression, anti-dripping, and filling; second, its application in the environmental field. As an environmentally friendly product, due to its excellent performance, it has occupied the first place in the consumption of magnesium hydroxide. Magnesium hydroxide has strong adsorption, high activity, especially slurry-like products, which have the characteristics of non-precipitation, non-agglomeration, good fluidity, easy pumping and storage, and convenient use and adjustment control. It can be used for neutralization of acidic wastewater, removal of heavy metals, flue gas desulfurization, treatment of acid rain on land, and pH adjustment. The specific uses of magnesium hydroxide can be divided into the following categories:
- Application in Flame Retardancy: Currently, the flame retardants actually used mainly include halogen-based, organophosphorus-based, and inorganic antimony-based, aluminum-based, magnesium-based, boron-based, and molybdenum-based flame retardants. Among them, halogen-based (mainly bromine-based) flame retardants are one of the organic flame retardants with the largest output in the world. The synthetic materials using organic flame retardants will emit toxic gases and thick smoke during combustion, threatening human life and property safety. Moreover, the production process of organic flame retardants is difficult to control, the waste is easy to cause environmental pollution, and the production cost is high. Magnesium hydroxide, however, is a halogen-free flame retardant. It decomposes by absorbing heat and generating water when heated, and no corrosive or harmful substances are generated after decomposition. It can not only increase the decomposition temperature of the filled material but also does not cause pollution to the environment. It can be widely used in the flame retardancy and smoke suppression of polymer materials such as polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and unsaturated resins. Magnesium hydroxide has a high thermal decomposition temperature, which is beneficial to accelerate the extrusion speed and shorten the molding time. At the same time, it also helps to improve the flame retardancy efficiency and can be widely used in polyester, epoxy resin, coatings, fiber products, polypropylene, polyacrylonitrile, polyvinyl acetate, wires, cables, wood, rubber, paint, polyvinyl chloride and other fields.
- Treatment of Sulfur-Containing Wastewater: Magnesium hydroxide is a weak alkali, and slurry-like magnesium hydroxide has the advantages of non-precipitation, non-fluidity, and convenient use and adjustment. The weak alkalinity of magnesium hydroxide gives it a unique buffering and neutralizing capacity. The pH value will not exceed 9 during use, which is exactly the highest limit allowed for effluents in the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s “Clean Water Acts”, while other alkaline substances will cause the pH to reach above 12 if excessive. Magnesium hydroxide has a slow neutralization speed, the neutralized particles settle quickly, are easy to filter, and have strong adsorption capacity, high activity, and low corrosiveness. These advantages enable magnesium hydroxide to reduce operating procedures and time and reduce equipment investment in the treatment of acidic wastewater. Therefore, magnesium hydroxide can be widely used in the treatment of acidic wastewater.
- Heavy Metal Removal Agent: Due to its large specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity, magnesium hydroxide is easy to adsorb and remove heavy metal ions such as Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, and Cr6+ that are harmful to the environment from various industrial waste liquids. Magnesium hydroxide can be used alone or in combination with lime, bentonite, etc. As a heavy metal removal agent, a Japanese patent detailed the unique features of using magnesium hydroxide and pointed out its incomparable superiority over treatment with Ca(OH)2.
- Flue Gas Desulfurization: The use of magnesium-based materials for desulfurization originated in Japan and has now become a common concern and research topic internationally. Air pollution mainly comes from the waste gas produced by combustion. Most waste gases, especially those from coal combustion, contain a large amount of sulfur dioxide. Since the 1980s, slurry-like magnesium hydroxide products have emerged in flue gas desulfurization. This is because, compared with other methods, the use of magnesium hydroxide for desulfurization has the advantages of high efficiency, convenient operation, relatively simple process, recyclable by-products, and high economic benefits.
- Decolorization of Printing and Dyeing Wastewater: Printing and dyeing wastewater is a type of industrial wastewater that is extremely harmful to the environment, with large discharge, complex composition, and deep color, especially various dyes with good water solubility and strong coloring power, making traditional treatment methods difficult to be effective. In recent years, research on the use of magnesium hydroxide to treat printing and dyeing wastewater has been carried out at home and abroad. The basic principle is to use positively charged Mg(OH)2 to adsorb negatively charged anionic dyes to decolor the dye wastewater.
- Wastewater Dephosphorization and Deammoniation: Phosphates in wastewater will promote algal growth, leading to oxygen depletion in fish, and ammonia will harm the survival of marine organisms. Excessive discharge of phosphorus and ammonia has caused serious eutrophication and red tide phenomena in major lakes and oceans in China. Therefore, the content of ammonia and phosphorus must be reduced before wastewater discharge. Magnesium compounds such as magnesium hydroxide, light-burned magnesium oxide, and dolomitic lime (MgO·CaO) have significant effects on phosphorus and ammonia removal.
- Others: Using magnesium hydroxide, an intermediate product in the seawater magnesia production process, as an adsorbent can pre-remove about 80% of boron from seawater, laying an important foundation for the subsequent production of low-boron magnesia. In chemical pulp bleaching, magnesium hydroxide can be used as an alkali agent and cellulose protective agent to reduce the COD content in wastewater and increase the pulp viscosity while maintaining the final whiteness of the pulp. Magnesium hydroxide can also be used as a fresh-keeping and antiseptic agent for meat products, feed, and feed additives containing fat and protein, and can also be used in combination with antioxidants to prevent biodegradation of meat tissue and maintain elasticity and tenderness. As a potato preservative, coating the surface of potatoes with a 3% magnesium hydroxide emulsion as a non-toxic protective layer at 4℃~6℃ can effectively prevent diseases caused by plant pathogens. In addition, magnesium hydroxide has some applications in oil exploitation as a component of new oilfield mud materials, as well as in pharmaceutical and cosmetic products, cigarette paper, smoke-suppressing coatings, and magnetic material processing.
