Messi Biology stated that magnesium oxide (MgO), as an inorganic compound, is mainly used in deodorants based on its excellent physical and chemical properties. Magnesium oxide has strong adsorption, chemical stability and antibacterial effects, and can effectively adsorb, convert or neutralize odorous molecules. The deodorizing mechanism of magnesium oxide will be developed in detail below, including adsorption, chemical reactions and other auxiliary mechanisms.
1. Adsorption
The core of the deodorization performance of magnesium oxide lies in its excellent adsorption ability. Magnesium oxide is a substance with a large specific surface area, so it can adsorb odor molecules in the air through physical adsorption. The surface of magnesium oxide has some tiny pores that can capture and encapsulate odor molecules, such as ammonia (NH₃), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), etc. The specific mechanism is as follows:
Physical adsorption: The surface of magnesium oxide has certain hydrophilicity and lipophilicity, and can adsorb moisture, oily substances and gas molecules. Through this physical adsorption, odor molecules are adsorbed to the surface of magnesium oxide, thereby reducing their concentration in the air.
Pore adsorption: The microporous structure of magnesium oxide can capture gas molecules on its surface, and this “adsorption effect” is similar to the effect of activated carbon. Through this mechanism, magnesium oxide can effectively adsorb odor molecules such as ammonia and sulfide to reduce odor in the air.
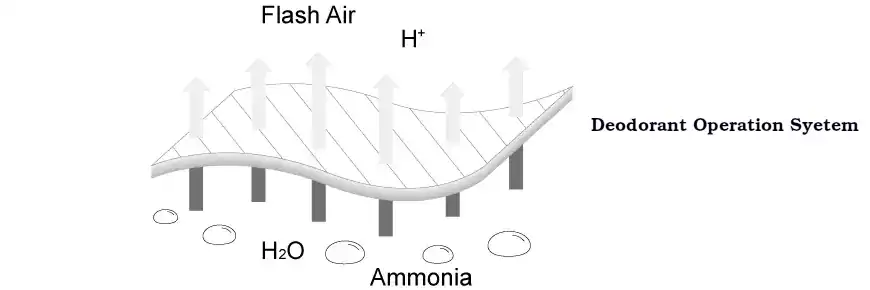
2. Acid-base reaction neutralizes odor
Magnesium oxide is highly alkaline and can react with acid gases in the air to neutralize and eliminate odor. For example:
Ammonia (NH₃): Ammonia is a common foul-odor gas that is widely present in cat litter, urine and other places. Magnesium oxide can react with ammonia to form amino compounds or chlorides, thereby neutralizing their odor. Through this chemical reaction, ammonia is converted into odorless compounds, thereby removing the odor.
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S): Hydrogen sulfide is a gas with a strong odor and is commonly found in rotten organic matter. The alkalinity of magnesium oxide can react with hydrogen sulfide to form odorless magnesium sulfide (MgS). Through this chemical reaction, magnesium oxide can effectively remove the odor of hydrogen sulfide.
3. Antibacterial and inhibit microbial growth
Magnesium oxide not only adsorbs odor molecules, but also has certain antibacterial effects. This antibacterial action also helps remove odors caused by bacteria or fungi. When magnesium oxide reacts with moisture, magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) will be produced. Magnesium hydroxide is alkaline and can inhibit the growth of certain bacteria and fungi and reduce the odor they produce. For example, magnesium oxide can effectively inhibit the growth of spoilage and mold-related bacteria (such as E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus) and reduce the foul-odor molecules they produce in the air.
4. Suspended release deodorization effect
Magnesium oxide can slowly release its adsorbed gas, which allows magnesium oxide to provide a lasting deodorant effect in deodorant products. Compared with other traditional deodorants, the deodorization effect of magnesium oxide can last for a long time, avoiding the trouble of frequently changing the deodorant. This sustained release mechanism of magnesium oxide allows it to maintain an effective removal of odor in the air for a long time.
5. Hygroscopicity and moisture management
Magnesium oxide has a certain hygroscopicity. It can absorb moisture in the air and prevent moldy or damp odor caused by moisture. Moisture is the source of many odors, especially in enclosed spaces (such as wardrobes, shoes, pet areas, etc.). Magnesium oxide reduces moisture accumulation through hygroscopic function, thereby reducing the occurrence of mold, bacteria and odor.
6. Synergistic effect of magnesium oxide and other deodorizing ingredients
Magnesium oxide can not only play a deodorizing effect alone, but also work in concert with other deodorizing ingredients to enhance the overall deodorizing effect. For example, when magnesium oxide is combined with activated carbon, bamboo charcoal or natural minerals, multiple deodorization mechanisms can be formed to maximize its deodorization effect. The adsorption properties and chemical reaction capabilities of magnesium oxide can complement the physical adsorption or chemical decomposition mechanisms of other materials, thereby achieving a more comprehensive deodorization effect.
7. Removal of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Magnesium oxide can remove some volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as benzene, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde and other toxic and harmful gases. These organic compounds are usually the source of indoor air pollution, and magnesium oxide can effectively reduce the concentration of VOCs through chemical reactions or adsorption on its surface. Especially in newly renovated houses or environments with strong chemical odors, magnesium oxide can play an important role in removing them.
