The preparation of magnesium carbonate and magnesium oxide whiskers usually involves multiple steps and can be achieved by different methods. Here is a brief overview of two common preparation methods and the key points of their morphology control:
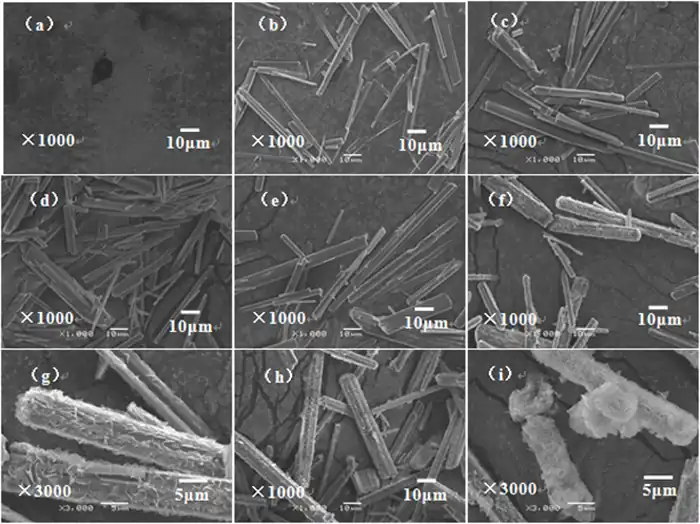
Preparation of magnesium carbonate whiskers
1. Raw material preparation: Magnesite, ammonium sulfate and ammonia water are used as the main raw materials.
2. Preparation of magnesium sulfate solution: Refined magnesium sulfate solution is obtained through calcination, dissolution, purification and other processes.
3. Precipitation synthesis: Magnesium carbonate whiskers are synthesized by precipitation method using magnesium sulfate solution as raw material. This usually involves mixing magnesium sulfate solution with ammonium bicarbonate (NH4HCO3) solution and then adjusting the pH value to an appropriate range (such as 9.5) to promote the formation of magnesium carbonate.
4. Morphology control: Reactant concentration, reactant ratio, reaction time and reaction conditions (such as temperature) will affect the morphology of the final product. For example, a higher pH value may lead to the formation of more slender whiskers.
Preparation of magnesium oxide whiskers
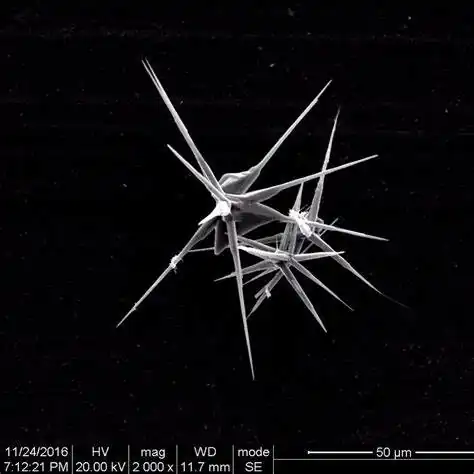
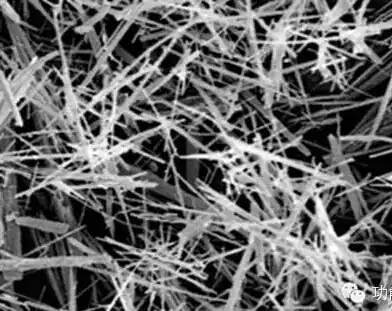


1. Precursor preparation: First, hydrated magnesium carbonate whiskers are prepared as precursors.
2. Calcination: Under the condition of no protective atmosphere, the precursor is burned in a muffle furnace by controlling the calcination temperature and time to obtain well-crystallized magnesium oxide whiskers.
3. Morphology control: The morphology of the precursor is one of the important factors that determine the final magnesium oxide whisker morphology. In addition, the calcination temperature and time will also significantly affect the length and diameter of the whiskers.
Key points of morphology control
• Reaction conditions: including temperature, pH value, reaction time, etc., which directly affect the growth direction and rate of whiskers.
• Precursor selection: Selecting a suitable precursor material, its own morphology will affect the morphology of subsequent products.
• Post-processing process: steps such as washing, drying and calcination will also affect the properties of the final product.
By finely controlling the above parameters, the size, length and diameter of the whiskers can be effectively controlled to meet the needs of different applications.
