The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has the largest cobalt resources reserves in the world, and its production capacity accounts for more than half of the world’s total production. Cobalt resources in the DRC mainly exist in the form of copper-cobalt cobalt ores, with a small number of individual cobalt ores.

The wet smelting of copper and cobalt ores generally adopts the leaching-extraction-electrowinning process to produce copper cathode, and the cobalt-containing residual liquid after copper extraction is generally used to produce cobalt salts or cobalt compounds by the process of removing impurities and cobalt precipitation.
In addition to impurity process is generally used in the neutralization and hydrolysis meta-precipitation method can be removed from the ferrous ions and Yu ions and other impurities in the folder solution, neutralization and the agent is generally used in lime or slaked lime, oxidation in addition to impurities (iron, manganese, etc.) methods usually have a mixture of sulfur dioxide and air oxidation, oxidation of strong oxidizing agents (sodium chlorate, etc.) oxidation, sodium thiosulphate and air oxidation, etc., which oxidation of strong oxidizing agents can easily cause a high local potential resulting in the loss of valuable metal cobalt, sodium thiosulphate will be the most common oxidizing agent in the process of cobalt precipitation. The strong oxidizer oxidation method is easy to cause high local potential resulting in the loss of valuable metal cobalt, and sodium thiosulfate will introduce impurity sodium ions into the system. Sulfur dioxide and air oxidation method has the advantages of relatively low potential to avoid loss of cobalt and no introduction of impurity ions.
Cobalt precipitation processes generally use precipitants to separate cobalt ions from the solution by forming insoluble cobalt salts or cobalt compounds. Cobalt precipitation process usually used precipitant HS, sodium salt, etc. HS is toxic, hazardous to human health and easy to cause environmental pollution. Sodium salts such as Na, CO, NaOH and other alkaline, easy to form a solution localized into the pH into too high an environment, so that the solution of other impurities ions and cobalt ions precipitated down to the cobalt products in the cobalt grade is reduced, impurities on the high side, and the use of sodium salts will be introduced to the system of sodium ions is difficult to deal with the higher concentration of sodium ions on the production of adverse effects. Activated magnesium oxide has a weak alkalinity, the use of relatively safe, and cobalt precipitation wastewater is easier to deal with.
This paper provides a cobalt-containing extracted liquid decontamination, a section of magnesium oxide cobalt precipitation, two slaked lime cobalt precipitation, slaked lime magnesium precipitation of the new process to produce high-grade cobalt hydroxide, focusing on the study of magnesium oxide additive amount of cobalt precipitation of a section of the impact, and according to the whole process of organizing the trial production. Trial production results show that the selected process is suitable for the production of high-grade cobalt hydroxide, a section of cobalt precipitation cobalt hydroxide products with a cobalt grade of 32%, the cobalt recovery rate of the whole process reaches 96%, and magnesium precipitation wastewater can be returned as production water.
1、Raw materials and auxiliary materials
1.1 Raw material
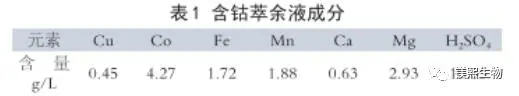
Cobalt sulfate solution for production is the cobalt-containing stem residue of a copper-cobalt mine in Congo (D.R.) after stirring leaching and extraction, and its typical chemical composition is shown in Table 1.
1.2 Into the main auxiliary materials
Slaked lime: industrial use, -200 mesh>90%, CaO>70%;
Magnesium oxide: industrial use, -325 mesh>99%, MgO>90%;
Sulfur dioxide: acid production flue gas (SO₂ concentration 7.5%).
2、Treatment process
The treatment process mainly consists of removing impurities, one section of cobalt precipitation, two sections of cobalt precipitation, magnesium precipitation and cobalt hydroxide drying and other processes. De-hybridization is to add slaked lime to the cobalt-containing extract, and pass a certain proportion of sulfur dioxide and air mixture, so that the solution of low-valent iron, manganese ions oxidized into high-valent iron, manganese ions, hydrolysis occurs at a certain pH to form a precipitate and separation of cobalt ions with the valence of cobalt ions. One stage of cobalt precipitation is to add magnesium oxide to the solution after removal of impurities, so that the cobalt ions in the solution into the precipitation to get cobalt hydroxide products. The second section of cobalt precipitation is to add quicklime to the liquid after one section of cobalt precipitation to recover the cobalt ions which have not been precipitated completely, and the cobalt residue of the second section returns to the iron removal and re-dissolves into the liquid after the removal of impurities. Magnesium precipitation is to add quicklime to the second section of the cobalt precipitation after the liquid to remove magnesium ions and other impurities in the solution, to realize the magnesium wastewater reuse, magnesium dregs are stored separately.

